A 3D shape is a mathematical representation of an object in 3D space, that is described by its edges, faces, and vertices.

A face is a 2D shape that makes up one surface of a 3D shape, an edge is where two faces meet and a vertex is the point or corner of a geometric shape.
A wireframe model is an edge or skeletal representation of an object.
3D Coordinate Space and Axes
The 3D dimensional space that applications like Maya and Unreal rely on is based on the cartesian coordinate system. Using this system, space is defined by using 3 axes (x, y and z – representing width, height and depth accordignly).

Mesh Construction
The group of faces that make up a 3D model is what we call a Mesh.
The number of faces in a mesh isknown as the poly count, and the polygon density is referred to as the resolution.
All 3D models are made from primitives that are extruded, bavelled and scaled, sculpted etc. The edges, faces and vertices of a primitive are manipulated in such way to create a certain shape.
 Primitives are the building blocks of 3D basic geometric forms, that you can use as is or modify to your liking. Most software packages build them in for speed and convenience.
Primitives are the building blocks of 3D basic geometric forms, that you can use as is or modify to your liking. Most software packages build them in for speed and convenience.
The most common 3D primitives are cubes, pyramids, cones, spheres, and tori, which are building blocks for more complex forms.
VECTARY is a great free online basic modelling software used to create, share and customise 3D models with easy-to-use tools. It is a great starting point to understand how shapes are made and to get a feel of vertices, edges and faces.
As I said above, when making a 3D model, primitives are extruded, bavelled and scaled, sculpted etc. in such way to create the desired shape.
Extruding
An extrusion is simply pushing a 2D shape into the third dimension by giving it a Z-axis depth. The result of an extrusion is a 3D object with width, height, and now, depth.
Bevelling
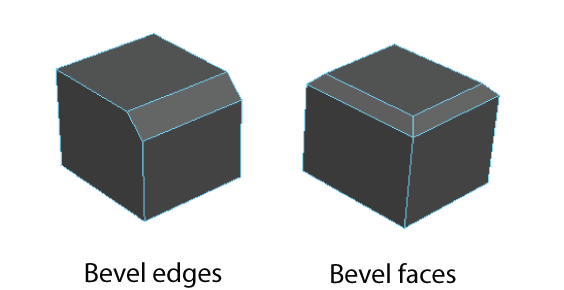 Bevels expand each selected edge into a new face, rounding the edges of a polygon mesh
Bevels expand each selected edge into a new face, rounding the edges of a polygon mesh
Scaling
Use Scale to adjust the overall size of an object. Like other transforms, the results of a scale operation may vary according to the coordinate system, axis constraint settings, and pivot point. For example, if the X-axis is the only one active, a scale stretches the object horizontally only. If all three axes are active, scale re-sizes the object in all directions.
Rotating
Rotate makes an object revolve around the selected axis. The tricky part about Rotate is making sure everything is set up so that the object revolves in the way you want.
Positioning
Positioning relocates objects, allowing you to place shapes and objects anywhere in the 3D world.
Insert Edge-Loop
 The Insert Edge Loop Tool lets you select and then split the polygon faces across either a full or partial edge ring on a mesh. It is useful when you want to add detail across a large area of a mesh or when you want to insert edges along a user-defined path.
The Insert Edge Loop Tool lets you select and then split the polygon faces across either a full or partial edge ring on a mesh. It is useful when you want to add detail across a large area of a mesh or when you want to insert edges along a user-defined path.
Box Modeling vs Extrusion Modeling
Box modeling is a technique in 3D modeling where a primitive shape is used to make the basic shape of the final model, which is then used to sculpt out the final model. The process uses subdividing to reach the final product, which can lead to a more efficient and more controlled modelling process.
Box modeling is a modeling method that is quick and easy to learn. It is also appreciably faster than placing each point individually. However, it is difficult to add high amounts of detail to models created using this technique without practice.
Extrusion modeling is also a technique where a model is created from a primitive shape. but rather than adding subdivisions, like with box modeling, new geometry is created through extrusion
 These two techniques are usually used together to create accurate and complex 3D models.
These two techniques are usually used together to create accurate and complex 3D models.
There is a range of other modeling techniques used to create 3D objects, these include: edge modeling, nurbs modeling (created by bezier curves), digital modeling, image based modeling and 3D scanning.
Modeling a LootBox
To model a loot box I started off with a (Primitive Object) Cube, positioned it in the middle of the world, scaled it properly and rotated it to match the world axis. I then added a few edge loops, selected some faces and extruded them. Finally, to add final details, I bevelled the edges. To create this lootbox I used both box modeling and extrusion modeling techniques together.